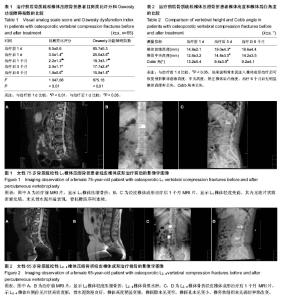
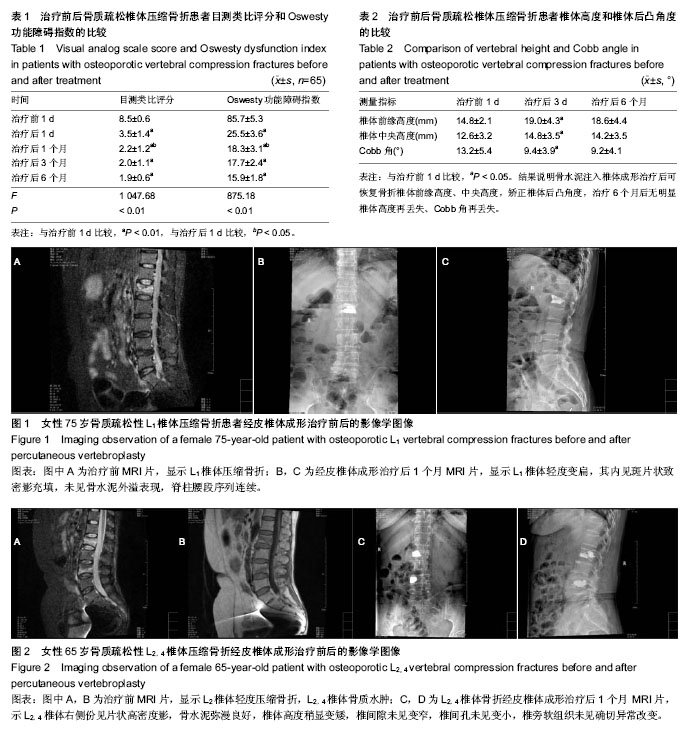
| [1] 高超,王联营,田治海,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床及影像学分析[J].现代医用影像学,2009,18(4):234-236.
[2] 蒙家辉,张文作.骨质疏松症腰背痛的治疗进展[J].右江民族医学院学报,2009,31(2):279-280.
[3] 张嘉,李强,张杰石.骨质疏松性陈旧脊柱压缩骨折:保守治疗还是椎体强化[J].中国骨与关节外科,2013,6(2):148-152.
[4] Rousing R,Hansen KL,Andersen MO,et al.Twelve-months follow-up in forty-nine patients with acute/semiacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated conservatively or with percutaneous vertebroplasty: a clinical randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2010;35(5):478-482.
[5] 王丰斌.经皮椎体形成术(PVP)与保守治疗方法在治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的疗效比较[J].航空航天医学杂志,2013,24(10): 1205-1207.
[6] 张豪伟,刘帅,董胜利.经皮微创与后路开放手术治疗单节段胸腰椎压缩骨折疗效分析[J].中国实用医刊,2013,40(3):7-9.
[7] Kostuik JP,Errico TJ,Gleason TF.Techniques of internal fixation fordegenerative conditions of the lumbar spine.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1986;203:219-231.
[8] Rousing R,Andersen MO,Jespersen SM,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared to conservative treatment in patients with painful acute or subacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: three-months follow-up in a clinical randomized study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009;34(13):1349-1354.
[9] Kloc W,Libionka W,Pierzak O,et al.The effectiveness of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of different aetiology Vertebral Body Fractures. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2012;176(9):372-374.
[10] Voormolen MH,Lohle PN,Fransen H,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: first short term results.Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd.2003;147(32):1549-1553.
[11] 刘达,潘显明,廖冬发,等.不同剂量聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥强化骨质疏松人工骨模块中椎弓根螺钉稳定性的研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(14):6477-6480.
[12] 姚维芳,王宇仁,沈云.β-磷酸三钙的加入对玻璃基生物骨水泥显微结构的影响[J].脊柱外科杂志,2007,5(5):298-301.
[13] 葛付涛,赵松,牛丰,等.磷酸钙骨水泥球囊撑开椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(2):128-132.
[14] 胡成栋,刘曦,周玉军,等. 椎体成形治疗中聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(21):3823-3830.
[15] 高万露,汪小海.视觉模拟疼痛评分研究的进展[J].医学研究杂志, 2013,42(12): 144-146.
[16] 许斌,王与荣,赵建宁,等.ODI在腰椎间盘突出症手术疗效评价中的应用[J].颈腰痛杂志,2004,25(1):31-34.
[17] Omidi-Kashani F,Hasankhani EG,Ebrahimzadeh MH,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty in Iranian patients with osteoporotic vertebral fractures.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2013; 1(1):9-13.
[18] Saracen A,Kotwica Z.Treatment of multiple osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures by percutaneous cement augmentation.Int Orthop.2014 .[Epub ahead of print]
[19] Joseph RN,Swift AJ,Maliakal PJ.Single centre prospective study of the efficacy of percutaneous cement augmentation in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures.Br J Neurosurg.2013;27(4):459-464.
[20] Chou KN,Lin BJ,Wu YC,et al.Progressive kyphosis after vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(1):68-73.
[21] Klazen CA,Lohle PN,de Vries J,et al.Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial.Lancet.2010;376(9746):1085-1092.
[22] Song D,Meng B,Gan M,et al.The incidence of secondary vertebral fracture of vertebral augmentation techniques versus conservative treatment for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Radiol. 2014.pii: 0284185114544240.[Epub ahead of print]
[23] 张志勇,孙晓威,解光越,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗老年人骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床疗效研究[J].中华老年医学杂志,2013, 32(4):419-422.
[24] 黄昊,何仕诚,方文,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松疼痛性椎体压缩骨折的临床疗效分析[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(27):2119-2122.
[25] Patil S,Nene AM.Predictors of kyphotic deformity in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a radiological study.Eur Spine J. 2014.[Epub ahead of print]
[26] Kim JH,Yoo SH,Kim JH.Long-term Follow-up of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Osteoporotic Compression Fracture: Minimum of 5 Years Follow-up.Asian Spine J. 2012;6(1):6-14.
[27] Tie B,He SC,Teng GJ,et al.Cement leakages in percutaneous vertebroplasty:analysis of postoperative computed tomography.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.2012;92(5):299-302.
[28] Baumann C,Fuchs H,Kiwit J,et al.Complications in percutaneous vertebroplasty associated with puncture or cement leakage.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007;30(2): 161-168. |